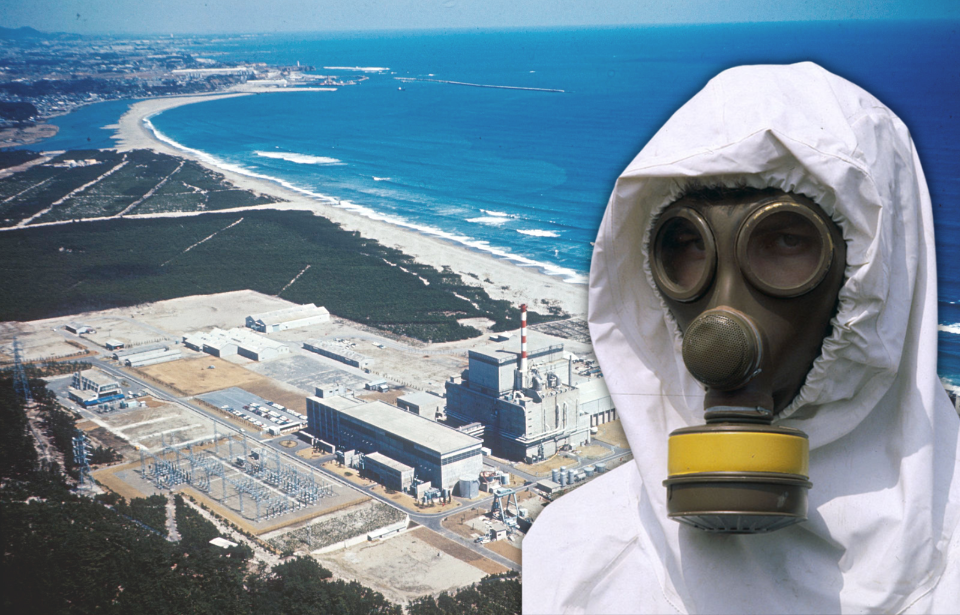
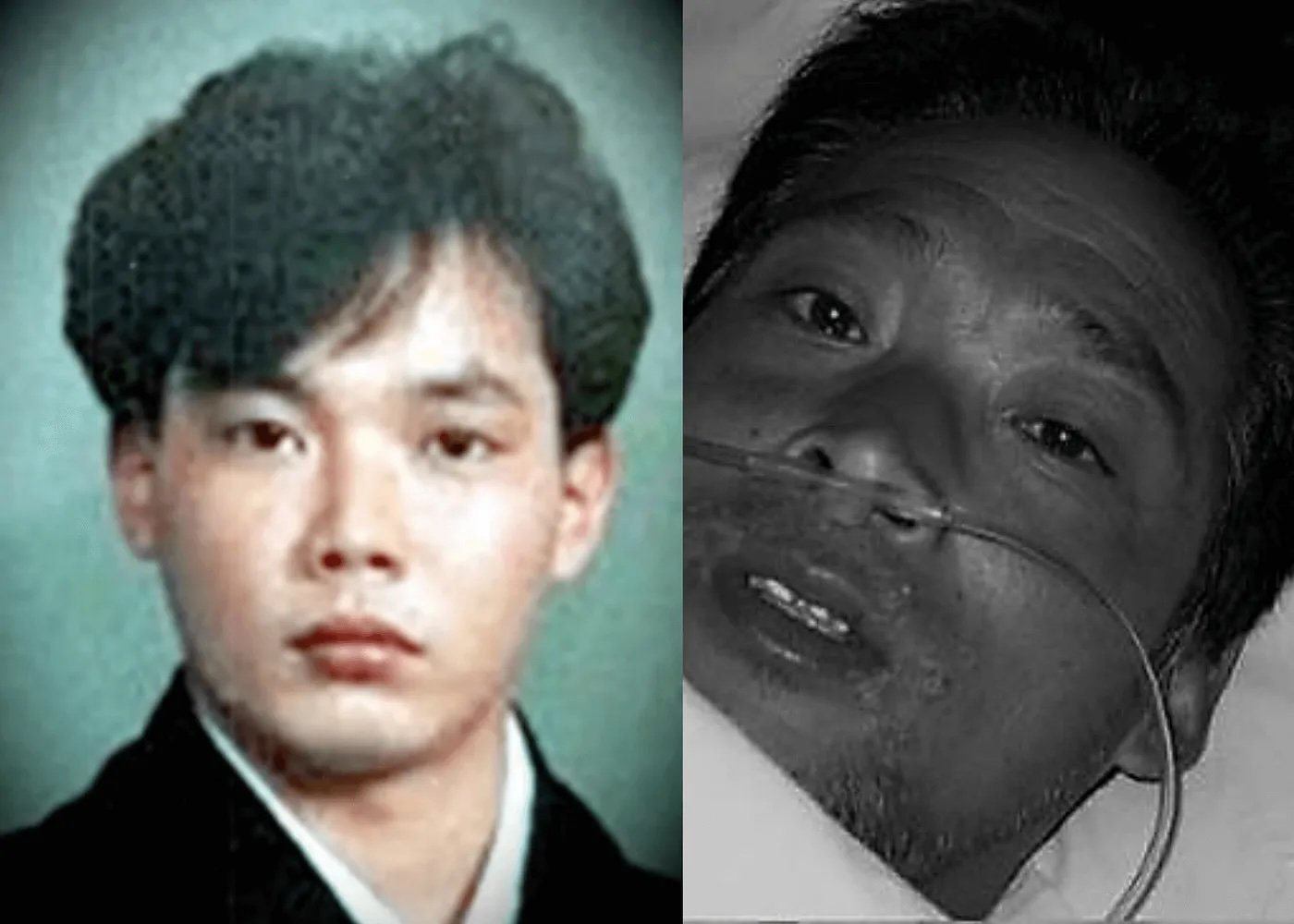
The case of Hisashi Ouchi remains a poignant reminder of the dangers posed by improper handling of nuclear materials. His body became a symbol of the severe consequences of nuclear accidents, drawing global attention to the critical importance of safety protocols. This article explores the tragic events that unfolded, their profound implications, and the enduring lessons they offer for the future of nuclear technology.
The story of Hisashi Ouchi is frequently referenced in discussions about radiation safety and the management of nuclear facilities. To fully appreciate the significance of this case, it is crucial to examine the broader context of nuclear accidents and their lasting impact on both human health and the environment.
This article aims to provide a detailed examination of Hisashi Ouchi's experience, the complex medical challenges faced during his treatment, and the lessons that have shaped modern nuclear safety practices. By delving into this case, we hope to emphasize the critical role of safety measures in safeguarding nuclear facilities worldwide.
Read also:Understanding Lichtenberg Figure Scars Causes Treatment And Prevention
Table of Contents
The Incident: What Happened to Hisashi Ouchi
Understanding Radiation Exposure
Medical Challenges Faced by Hisashi Ouchi
Treatment and Care for Radiation Victims
Lessons Learned from the Hisashi Ouchi Case
Read also:Why Funny Cat Memes Are A Universal Source Of Joy
Long-Term Impacts of Radiation Exposure
Prevention and Safety Measures in Nuclear Facilities
Global Reactions and Responses
Conclusion: Moving Forward with Knowledge
Biography of Hisashi Ouchi
Hisashi Ouchi was a diligent worker at the Tokaimura nuclear plant in Japan, leading a modest life until the tragic events of September 30, 1999. Born on January 27, 1968, Ouchi's life was forever altered on that fateful day. Below is a summary of his personal background:
| Full Name | Hisashi Ouchi |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | January 27, 1968 |
| Occupation | Worker at Tokaimura Nuclear Plant |
| Place of Incident | Tokaimura, Japan |
| Date of Incident | September 30, 1999 |
Early Life and Career
Prior to the incident, Hisashi Ouchi was a committed employee at the Tokaimura nuclear facility. He worked tirelessly to support his family and contribute to the operations of the plant. However, his dedication to his career led him to one of the most catastrophic radiation exposure cases in history, forever altering the course of his life.
The Incident: What Happened to Hisashi Ouchi
On September 30, 1999, Hisashi Ouchi and two colleagues were involved in a devastating accident at the JCO nuclear fuel processing plant in Tokaimura, Japan. The workers inadvertently triggered a criticality accident by mixing uranium oxide solution in a precipitation tank, exceeding the critical mass threshold. This resulted in an uncontrolled chain reaction, releasing lethal doses of radiation.
Sequence of Events
- The workers were preparing uranium fuel for reactors, following a routine procedure.
- They mixed the uranium solution in a precipitation tank, unaware of the impending danger.
- The mixture exceeded the critical mass, initiating a chain reaction that could not be stopped.
- Hisashi Ouchi was exposed to approximately 17 sieverts of radiation, a dose far beyond survivable limits.
Understanding Radiation Exposure
Radiation exposure occurs when an individual is exposed to ionizing radiation, which can cause significant harm to living tissues. In Hisashi Ouchi's case, the radiation dose was catastrophic, far exceeding the survival threshold of 10 sieverts as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO). Understanding the types of radiation involved is essential to comprehending the severity of his exposure.
Types of Radiation
- Alpha Radiation: Low penetration but highly damaging if inhaled or ingested.
- Beta Radiation: Moderate penetration, capable of causing skin burns and internal damage.
- Gamma Radiation: Highly penetrating and capable of damaging internal organs and DNA.
- Neutron Radiation: Extremely harmful due to its ability to alter atomic structures.
Hisashi Ouchi was primarily exposed to gamma and neutron radiation, both of which are highly penetrating and cause extensive cellular damage.
Medical Challenges Faced by Hisashi Ouchi
Following the accident, Hisashi Ouchi was immediately transported to the University of Tokyo Hospital, where a team of specialists worked tirelessly to treat his severe radiation sickness. The medical challenges were unprecedented, as his body had suffered extensive cellular damage due to the radiation exposure.
Symptoms of Radiation Sickness
- Severe burns on the skin, resulting in extensive tissue damage.
- Bone marrow failure, leading to a compromised immune system and an inability to produce blood cells.
- Organ damage, affecting vital systems such as the liver, kidneys, and heart.
- Extreme fatigue and weakness, symptomatic of systemic failure.
Despite the best efforts of the medical team, Hisashi Ouchi succumbed to his injuries 83 days after the incident, highlighting the devastating impact of acute radiation exposure.
Treatment and Care for Radiation Victims
Treating victims of severe radiation exposure is an immense challenge, requiring advanced medical interventions and experimental treatments. In Hisashi Ouchi's case, doctors employed several innovative methods to address his critical condition, including bone marrow transplants and blood transfusions. These treatments aimed to restore his immune system and replace damaged tissues.
Key Treatments
- Bone Marrow Transplant: Attempted to replace damaged bone marrow and restore blood cell production.
- Antibiotics: Used to prevent and manage infections caused by a compromised immune system.
- Pain Management: Essential for alleviating the excruciating pain associated with radiation burns and tissue damage.
- Hydration and Nutritional Support: Critical for maintaining bodily functions during prolonged treatment.
While these treatments provided temporary relief, they were ultimately insufficient to overcome the extensive cellular damage caused by the radiation exposure.
Lessons Learned from the Hisashi Ouchi Case
The Hisashi Ouchi case serves as a stark reminder of the dangers inherent in nuclear technology and the importance of robust safety measures. Several key lessons have emerged from this tragedy, shaping the future of nuclear safety:
Improved Safety Protocols
- Stricter Regulations: Enhanced guidelines for the handling of radioactive materials to minimize risks.
- Comprehensive Training: Mandatory training programs for all nuclear plant workers to ensure adherence to safety protocols.
- Regular Inspections: Frequent audits and inspections to identify and address potential hazards before they escalate.
These measures have been implemented globally to prevent similar incidents, emphasizing the critical role of vigilance in nuclear operations.
Long-Term Impacts of Radiation Exposure
While Hisashi Ouchi's case involved acute radiation exposure, the long-term effects of lower-level exposure can also be devastating. Research conducted by organizations such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) highlights the potential for increased cancer risks and genetic damage in individuals exposed to radiation.
Health Risks
- Increased Cancer Risk: Exposure to radiation, even at low levels, can significantly elevate the likelihood of developing various forms of cancer.
- Genetic Mutations: Radiation exposure can cause mutations in DNA, potentially affecting future generations.
- Reproductive Issues: Radiation can impair fertility and lead to complications during pregnancy.
Regular monitoring and early detection are essential for individuals exposed to radiation, even at relatively low levels, to mitigate long-term health risks.
Prevention and Safety Measures in Nuclear Facilities
Preventing accidents in nuclear facilities requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating advanced technology, rigorous training, and stringent safety protocols. Modern nuclear plants employ multiple layers of safety systems to minimize the risk of incidents.
Key Safety Measures
- Redundant Safety Systems: Multiple fail-safe mechanisms to ensure continuous operation and prevent accidents.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Consistent upkeep of equipment and facilities to identify and address potential issues promptly.
- Employee Training and Certification: Ongoing education and certification programs to ensure all personnel are well-versed in safety procedures.
These measures have significantly reduced the likelihood of accidents in nuclear facilities, promoting a safer and more secure nuclear industry.
Global Reactions and Responses
The Hisashi Ouchi case drew international attention, prompting a reevaluation of nuclear safety standards worldwide. Governments and organizations responded by implementing stricter regulations, fostering international cooperation, and increasing transparency in nuclear operations.
International Efforts
- IAEA Safety Guidelines: Updated protocols and standards to enhance nuclear safety practices globally.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts to share knowledge, technology, and resources to improve nuclear safety.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives to educate the public about nuclear safety and dispel misconceptions.
These efforts have contributed to a safer nuclear industry, fostering trust and confidence in nuclear technology as a viable energy source.
Conclusion: Moving Forward with Knowledge
The tragic case of Hisashi Ouchi underscores the critical importance of safety measures in nuclear facilities. Through advancements in regulations, technology, and training, the nuclear industry has made significant strides in preventing similar incidents. By learning from this tragedy, we can ensure that future generations benefit from a safer and more secure nuclear energy landscape.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this article and explore additional resources on radiation safety, nuclear technology, and global efforts to enhance nuclear security. Together, we can honor Hisashi Ouchi's legacy by prioritizing safety and innovation in the nuclear industry.
For further reading, consider exploring articles on radiation safety, nuclear technology advancements, and global initiatives to improve nuclear security.